Key Takeaways
- Stroma and Stomata are both geopolitical boundaries, but they serve different regional roles within a country’s territorial management.
- Stroma refers to internal boundary divisions that separate administrative regions, often used for governance and jurisdiction purposes.
- Stomata denote border zones or transitional areas that facilitate interaction between neighboring regions, especially for trade or cultural exchange.
- The distinction between Stroma and Stomata impacts political stability, resource distribution, and regional cooperation strategies.
- Understanding these terms helps in analyzing how countries organize their internal and external territorial relationships effectively.
What is Stroma?

Stroma is a term used to describe internal, often administrative, boundaries within a country or a large political entity. These borders delineate different regions, provinces, or districts, helping to organize governance, resource allocation, and local administration. The concept of Stroma is crucial for maintaining order and facilitating regional development.
Historical Formation of Stroma
The creation of Stroma often reflects historical processes such as colonization, wars, or treaties that led to the division of territories. In many cases, these boundaries were drawn to serve political interests or to accommodate ethnic, linguistic, or cultural differences. For instance, the division of colonial territories into administrative regions was driven by colonial powers to manage resources and control populations more effectively.
Over time, some Stroma boundaries have evolved through political reforms or independence movements, leading to reorganization of internal borders. These changes can significantly impact regional identities and local governance structures. The stability of Stroma boundaries often depends on the historical legitimacy and acceptance by local populations.
In some instances, Stroma boundaries are marked by physical features like rivers or mountain ranges, which naturally divide regions. In others, they are purely administrative lines created through legislation. The process of establishing or modifying Stroma boundaries can sometimes lead to conflicts or disputes among regions or ethnic groups.
Understanding the historical context of Stroma helps in analyzing current governance challenges and regional development policies. It also informs debates about territorial integrity and autonomy within a nation-state.
Legal and Administrative Significance
Stroma serves as a basis for legal jurisdictions, impacting local governance, taxation, and public services. Administrative boundaries define the scope of authority for regional governments, influencing policy implementation. These borders are often documented in legal statutes, which specify their extent and governance structures.
In many countries, the delineation of Stroma is crucial for electoral processes, determining constituency boundaries and representation. Accurate boundary demarcation ensures fair political participation and resource distribution. Administrative boundaries also influence law enforcement jurisdiction, judicial districts, and public administration units.
In some cases, disputes over Stroma boundaries lead to legal challenges or negotiations, especially if the demarcation affects resource-rich areas or minority populations. International treaties or national legislation often govern the modification or recognition of these boundaries to prevent conflicts,
Moreover, the management of Stroma influences regional planning, infrastructure development, and disaster response strategies. Clear boundaries enable coordinated efforts among different administrative units, improving overall governance efficiency.
In essence, Stroma’s legal and administrative importance lies in its role as a foundational element of territorial organization that underpins political stability and service delivery.
Impact on Economic Development
The delineation of Stroma can directly influence regional economic activities by defining zones of control and resource management. Clear boundaries facilitate targeted development policies, investments, and infrastructure projects tailored to specific regions.
Regions separated by well-established Stroma can develop specialized industries, leveraging local resources without interference from neighboring areas. For example, a province rich in agriculture may prioritize farming infrastructure, while a neighboring region with mineral deposits focuses on mining facilities.
Conflicts or ambiguities in Stroma boundaries can hinder economic cooperation or lead to resource disputes, affecting overall growth. When boundaries are disputed or unclear, investments tend to be delayed or diverted to more stable regions.
Furthermore, the existence of internal boundaries influences transportation networks and trade routes, which are vital for regional economic integration. Although incomplete. Efficient movement of goods and services across Stroma boundaries requires diplomatic coordination and infrastructure development,
In some cases, governments establish special economic zones along Stroma boundaries to encourage cross-border collaboration and trade. Although incomplete. These zones often benefit from relaxed regulations and incentives designed to promote regional prosperity.
Understanding how Stroma boundaries shape economic policies helps in designing strategies for sustainable regional development and resource sharing initiatives.
Social and Cultural Implications
Stroma boundaries often reflect or influence the cultural and social identities of populations within regions. These borders can serve as markers of ethnic, linguistic, or historical communities, shaping regional identities and social cohesion.
In some cases, Stroma boundaries align with cultural differences, reinforcing community bonds and facilitating targeted cultural preservation efforts. Conversely, misaligned boundaries can lead to tensions or feelings of marginalization among minority groups.
The internal division of territories also impacts social services, education, and healthcare delivery, which are often organized along these boundaries. Ensuring equitable access across Stroma lines becomes crucial for social stability,
Border areas, especially where Stroma boundaries meet, can become zones of cultural exchange or conflict, depending on the history and current political climate. These zones may host diverse populations with varying degrees of integration and cooperation.
Community-based organizations often engage in cross-boundary initiatives to foster social cohesion and cultural understanding. Such efforts can mitigate conflicts arising from boundary disputes or historical grievances.
Overall, Stroma’s influence on social and cultural aspects underscores the importance of respectful and inclusive boundary management for peaceful coexistence.
What is Stomata?
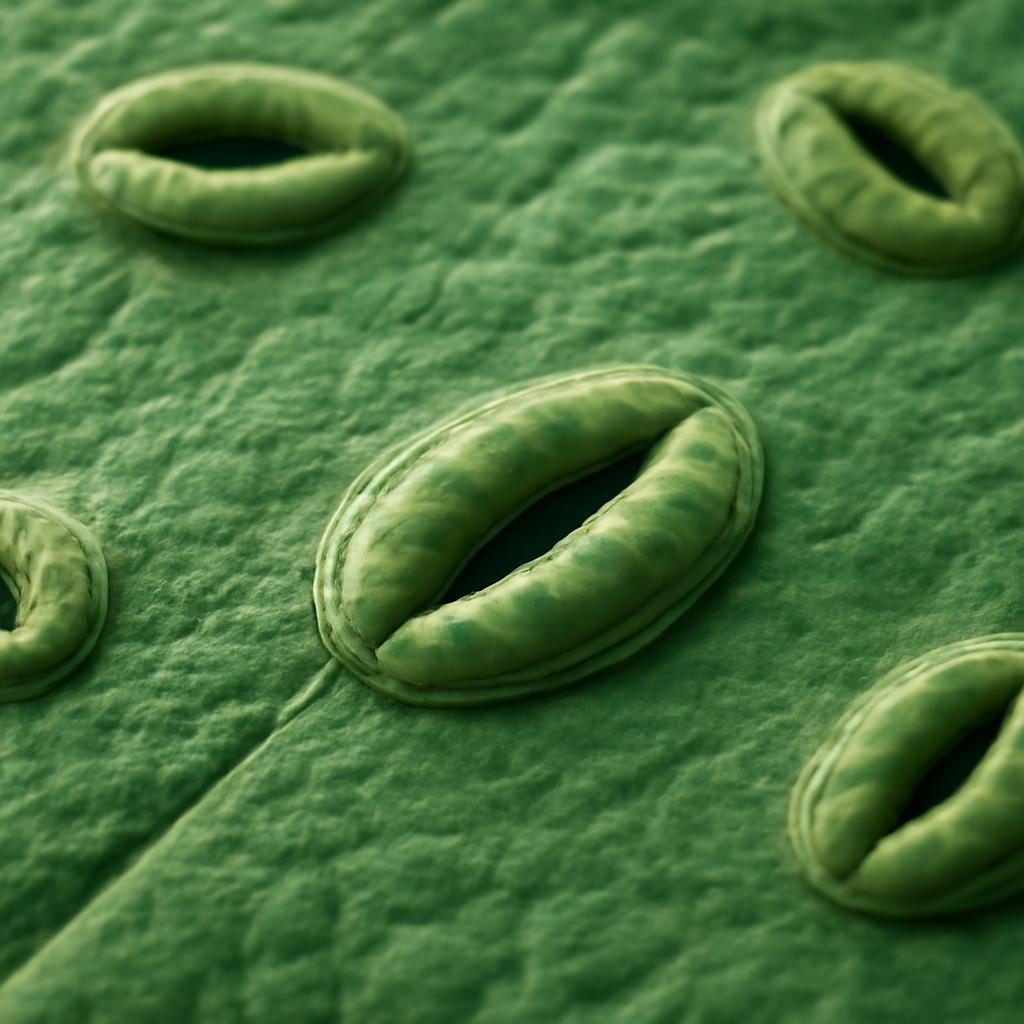
Stomata are not geopolitical boundaries but rather small openings or pores found on the surfaces of plant leaves and stems that regulate gas exchange. They are vital for controlling water vapor release and allowing carbon dioxide in for photosynthesis, playing a key role in plant survival.
Structure and Function of Stomata
Each stoma is surrounded by a pair of guard cells that control its opening and closing, responding to environmental stimuli like light, humidity, and internal plant signals. When conditions favor photosynthesis, guard cells swell, opening the pore to allow gas exchange. Conversely, during drought stress, they close to conserve water.
The size and density of stomata vary among plant species, influenced by environmental adaptations. Plants in dry environments tend to have fewer stomata or smaller openings to minimize water loss, while those in humid areas may have more open stomata for efficient gas exchange.
Stomatal regulation involves complex signaling pathways that respond to environmental cues. Hormones such as abscisic acid (ABA) play a role in signaling guard cells to close stomata during water deficiency.
Research into stomatal behavior helps scientists understand plant responses to climate change, especially concerning drought resistance and water use efficiency. Genetic modification of stomata characteristics is also explored to improve crop resilience.
Stomata function as dynamic gates that balance the plant’s needs for carbon dioxide with its water conservation strategies, critical for plant health and productivity.
Environmental and Agricultural Relevance
Stomatal activity directly impacts plant water use efficiency, influencing agricultural productivity, especially in arid or semi-arid regions. Farmers monitor stomatal behavior to optimize irrigation and reduce water waste.
Changes in atmospheric carbon dioxide levels can alter stomatal density and functioning, affecting plant growth patterns and crop yields. Elevated CO2 often leads to reduced stomatal density, which can modify water uptake and plant respiration.
In crop breeding, selecting for optimal stomatal traits has become a strategy to develop varieties that withstand drought conditions while maintaining high productivity. This approach is vital amidst increasing climate variability.
Environmental stresses like pollution or high temperatures can disrupt stomatal function, leading to reduced photosynthesis and growth. Understanding these impacts guides efforts to improve plant resilience.
Stomatal research also contributes to modeling climate change projections by providing insights into how plant transpiration and carbon sequestration might shift in future scenarios. This knowledge aids in developing sustainable agricultural practices,
In essence, stomata serve as crucial interfaces between plants and their environment, influencing ecological balance and food security.
Comparison Table
Below is a detailed comparison of the key aspects distinguishing Stroma from Stomata:
| Parameter of Comparison | Stroma | Stomata |
|---|---|---|
| Type of boundary | Internal administrative borders within a country | Microscopic pores on plant surfaces |
| Primary function | Dividing regions for governance and resource management | Regulating gas exchange and transpiration |
| Physical form | Line or zone demarcations on maps or legislation | Small openings or pores on leaf surfaces |
| Impact on population | Defines jurisdiction and administrative authority | Controls water loss and CO2 intake for plants |
| Natural vs. artificial | Primarily artificial or legislatively created boundaries | Natural biological structures |
| Size and scale | Regional or national scale | Microscopic, visible only under microscopes |
| Relevance to environment | Influences political stability and resource distribution | Impacts plant health and ecological balance |
| Changeability | Subject to political or legislative modifications | Responsive to environmental stimuli, dynamic |
| Associated disciplines | Geopolitics, political science | Botany, plant physiology |
| Boundary markers | Legislative documents, physical markers like rivers | Cell structures, microscopic pores |
Key Differences
Below are the main distinctions between Stroma and Stomata:
- Nature of Boundaries — Stroma are internal territorial borders, whereas Stomata are microscopic plant pores.
- Functionality — Stroma organize regions within a country for administrative purposes, while Stomata control gas exchange and water regulation in plants.
- Physical Scale — Stroma are large-scale geographic lines, whereas Stomata are tiny structures only visible under microscopes.
- Legislative vs. Biological — Stroma boundaries are established through laws and maps, contrasting with the biological nature of stomata.
- Impact Scope — Stroma influence political stability and resource management, while Stomata affect plant survival and ecological processes.
- Changeability — Adjustments to Stroma involve legal and political processes, while Stomata respond instantly to environmental changes.
- Relevance to Society — Stroma are relevant for governance and territorial integrity, whereas Stomata are crucial for plant health and agricultural productivity.
FAQs
Can Stroma boundaries change over time, and how does that affect regions?
Yes, Stroma boundaries can be modified through legislative or political processes, often leading to shifts in regional governance, resource distribution, and local identities. Such changes may resolve disputes or create new administrative zones, affecting regional cooperation and development strategies.
Are there any environmental factors that influence the shape or size of Stomata in plants?
Environmental conditions such as humidity, temperature, and light levels directly affect stomatal behavior and density. Plants adapt their stomatal features over generations to optimize water use efficiency and photosynthesis under prevailing climate conditions.
How do disputes over Stroma borders impact international or national relations?
Disagreements over internal boundaries can lead to political tensions, legal battles, or even conflict if regions claim sovereignty over disputed areas. Diplomatic negotiations and legal resolutions are often necessary to maintain stability and prevent escalation.
Are there technological innovations that help in monitoring or managing Stroma and Stomata?
Advances in satellite imaging, GIS mapping, and microscopic imaging aid in accurately delineating Stroma boundaries and studying Stomata behavior. These technologies improve resource management, environmental monitoring, and agricultural practices across different scales.
